2025年4月10日,Xiaoan Cao等作为原著作者,在《BMC Microbiology》发表“Genome phylogenetic analysis of Brucella melitensis in Northwest China”论文。

研究要点
布鲁氏菌病对中国西北地区的公共卫生构成严重威胁,然而该地区绵羊和牦牛体内分离的羊种布鲁氏菌基因组系统发育与传播模式仍不明确。
本研究通过细菌学检测、传统生物分型及全基因组单核苷酸多态性(WGS-SNP)分析,系统描绘了西北地区菌株的谱系特征。
46株布鲁氏菌均被鉴定为羊种布鲁氏菌生物变种3,这些菌株分离自至少三种动物宿主(家畜与野生动物),表明羊种布鲁氏菌感染在西北地区广泛流行,宿主多样性为该病原体的传播与维持提供了理想生态位。
WGS-SNP分析将46株羊种布鲁氏菌划分为四个分支(C-I至IV),包含八种SNP基因型(STs),提示西北地区至少存在四个流行谱系。
全球WGS-SNP系统发育分析显示,所有西北地区菌株均属于基因型II,各分支菌株与既往西北地区分离株呈现高度遗传相似性。
本研究为"多重相似羊种布鲁氏菌谱系在西北地区人群与动物中持续流行"的观点提供了有力证据。
畜牧业经济发展加速了活畜及畜产品的跨区域流动,推动该疾病传播范围的扩大。
因此,亟需制定精准防控策略以应对当前严峻的流行态势。
图文速览
Table 1 Distribution of location, hosts, isolation time, species/biovars, STs, and number of strains involved in this study
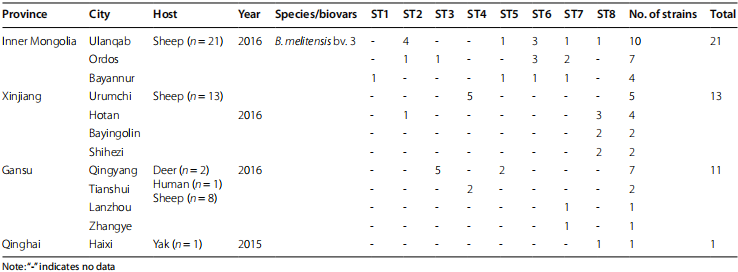
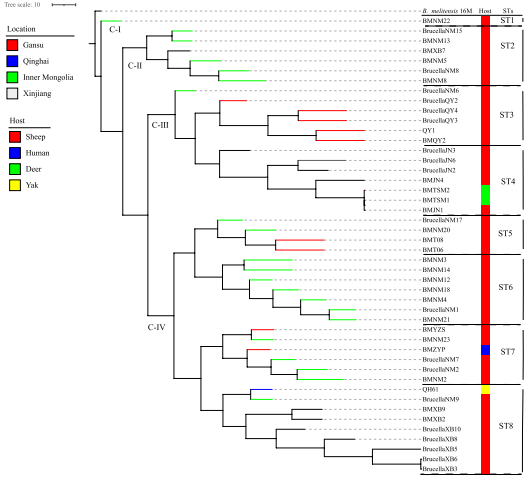
Fig 1 Maximum-likelihood tree generated from the cgSNP matrix of 46 B. melitensis samples at the county scale. Note: The phylogenetic trees of 46 B. melitensis strains were generated via TreeBeST via the maximum likelihood phylogenies (PHYML) algorithm with 1000 bootstrap replicates. Note: A branch marked by color indicates the location of strains isolated; the red branch indicates that strains are from Gansu; the blue branch indicates that strains are from Qinghai; the green branch indicates that strains are from Inner Mongolia; and the gray branch indicates that strains are from Xinjiang. The host spectrum is indicated in the right color column; the red column indicates strains from sheep, the blue column indicates strains from humans, the green column indicates strains from deer, and the yellow column indicates strains from yaks. ST1 - 8 indicates that strains are associated with each SNP genotype
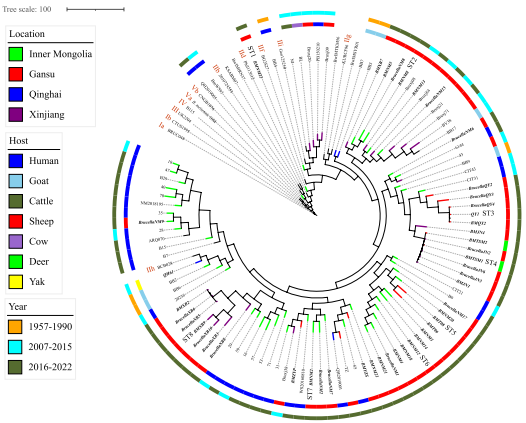
Fig 2 Phylogenetic analysis based on the maximum-likelihood tree of 110 B. melitensis strains at the global level. Note: The strains from GTs I–III refer to previously described methods [30] and are marked in red. The phylogenetic trees of 110 B. melitensis strains were constructed based on the maximum likelihood phylogenies algorithm with 1000 bootstrap replicates. Note: Among the 110 strains, 15 strains from GenBank display the five SNP genotypes (I–V, marked in red) of B. melitensis, and the remaining 95 strains were all isolated from Northwest China from GenBank. Strains from this study are marked with bold italics, and branches marked by color indicate the locations of the strains isolated; the green branch indicates that the strains are from Inner Mongolia; the red branch indicates that the strains are from Gansu; the blue branch indicates that the strains are from Qinghai; and the purple branch indicates that the strains are from Xinjiang. The host spectrum is marked in an inward circle, with humans in blue, gray in goats, dark green in cattle, red in sheep, light purple in cows, green in deer, and yellow in yaks. The years in which the strains were isolated are marked with external circles; the strains from 1957 to 1990 are marked with light yellow, the strains from 2007 to 2015 are marked with light blue, and the strains from 2016 to 2022 are marked with dark green
附件: